ALLERGIC GRANULOMATOSIS
What is allergic granulomatosis?
Allergic granulomatosis, also called Churg-Strauss syndrome (CSS), is a disorder than affects many body systems and is characterized by the prominence of allergic features, specifically:
- Rhinitis: Allergic nasal and sinus disease that causes nasal obstruction, recurrent sinusitis and nasal polyp fomation.
- Asthma: Reactive airway disease causing narrowing of the airways and inflammation making it difficult to breathe. This is the cardinal feature of CSS and occurs 8-10 years before the blood vessels become involved.
- Peripheral blood eosinophilia: This is the presence of higher than normal amounts of specialized immune-system cells, called eosinophils, in the blood. These eosinophils can cluster together and form nodules within the body called granulomas. Granulomas may form within the ear causing chronic ear inflammation and hearing loss
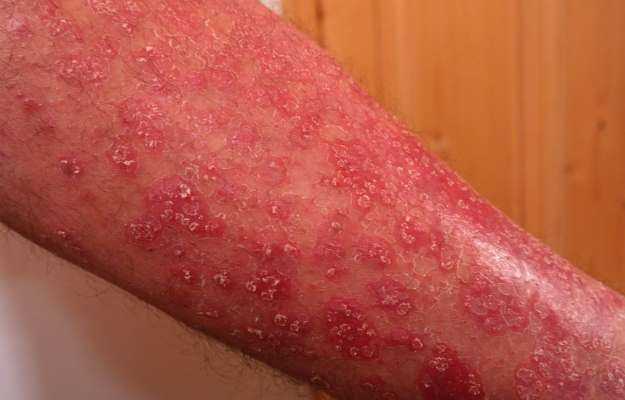
- Skin manifestations: One of the most common features of the vasculitic phase of CSS. Findings include:
- Subcutaneous nodules (granulomas) may form on the extensor surfaces of the arms, elbows, hands and legs.
- Palpable, small, red/purple bruise-like lesions called purpura.
- Flat or palpable red, erythematous rash
- Hemorrhagic lesions: these are bruise-like lesions that range in size from pinpoint spots to large patches.
CSS can affect any organ system but primarily targets the lungs and skin. It is characterized as a one the “vasculitides” meaning it is a subtype of a group of diseases that are characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis). There are 3 different phases of CSS, an individual may have one or all of these phases occurring at once:
- Prodromal phase: This occurs in people aged 10-20 years and is characterized by atopic disease (dermatitis), allergic rhinitis and asthma.
- Eosinophilic phase: This phase is defined by an increase in eosinophils in the blood (“peripheral blood eosinophilia”). These eosinophils then invade multiple organs, especially the lungs and intestinal tract. Symptoms include weight loss, fever, sweats, abdominal pain, diarrhea, bleeding and cough.
- Vasculitic phase: This occurs in people aged 20-30 years and is characterized by a life-threatening vasculitis of medium and small vessels. This is associated with granuloma formation in various organs and fever, weight loss, malaise and fatigue. Other symptoms include chest pain (cardiac involvement), joint pain (joint involvement), neurologic symptoms (nerve infiltrations) and cutaneous skin findings.
In severe cases CSS can affect other organs such as the heart, kidneys, muscles and digestive system.
What causes allergic granulomatosis?
The cause of CSS remains unclear. The disease is most likely an autoimmune process in which the body over-produces antibodies. In CSS these are called IgE antibodies and they are produced by eosinophils. Having a high amount of these IgE antibodies in your body causes allergic features of the disease to develop. In addition, these circulating antibodies clump together and form a complex of immune cells that deposit in the lungs, skin and blood vessels causing granulomas to form. A granuloma is a cluster of cells and debris, if located just under the skin they look like papules and nodules. Why a certain individual develops this disease is unknown, genetic factors are thought to play a role and some medications have been associated with development of CSS. Medications that alter the body’s allergy-inducing proteins (leukotrienes) may help unmask the disease.
How is allergic granulomatosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of allergic granulomatosis requires clinical findings and symptoms (asthma, rhinitis, skin rash) and lab tests. There are no lab tests that are specific for CSS, but when combined with clinical symptoms they can be helpful. Imaging studies such as chest x-rays can be helpful in visualizing lung granulomas and lung biopsy is considered the gold standard for the diagnosis of CSS. When looked at under the microscope a lung biopsy reveals patterns and features that are unique to CSS.
How is allergic granulomatosis treated?
The primary therapy for CSS is systemic glucocorticoids (steroids). Asthma is locally treated with inhaled glucocorticoids as well. Glucocorticoids work by suppressing the body’s immune response and are taken for 6 to 12 weeks or until disease symptoms have resolved. After an initial course of steroid therapy the patient may discontinue use and late relapses are uncommon. Some patients may need to take long-term steroid therapy.


