INGROWN TOENAILS
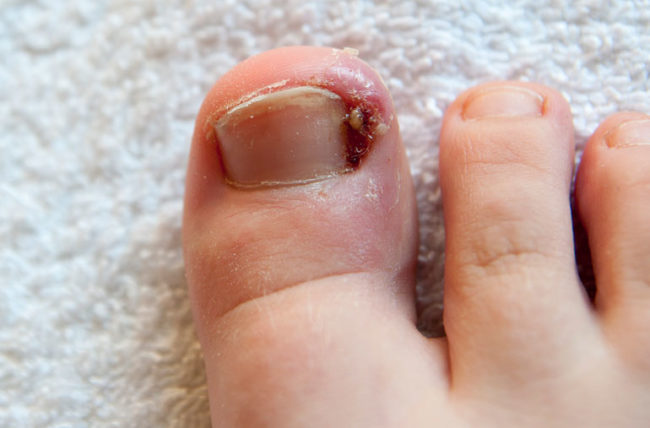
Definition: An ingrown toenail is a painful condition that occurs when a sharp corner of the toenail digs into the skin at the end of or side of the toe. Pain and inflammation at the spot where the nail cuts into the skin occurs first. Later, if left untreated, the inflamed area can begin to grow extra tissue or drain yellowish fluid. [1]
Causes
Several common causes of ingrown toenails include:
- Tight-fitting shoes or high heels. Tight shoes cause the toes to be compressed together and pressure is put on the nail. This can cause the nail to grow abnormally.
- Improper trimming of toenails. This can cause the corners of the nail to dig into the skin. Nails should be trimmed straight across and not rounded.
- Infections. Disorders such as fungal infections of the nail can cause a thickened or widened toenail to develop. [1]
- Injury. Either an acute injury near the nail or anything that causes the nail to be damaged repetitively can also cause an ingrown nail. Common acute injuries to the toenails include crush injuries.
- Genetics. If a member of your family has an ingrown toenail, then you are more likely to develop one. Some people have nails that are normally more rounded than others, which increases the chance of developing ingrown nails [1]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of an ingrown toenail include pain and tenderness around the nail, usually accompanied by redness and swelling. In severe cases there can also be an infection of the tissue around your toenail [2]
Complications
If left untreated, an ingrown toenail can progress to an infection or even an abscess that requires surgical incision and drainage. Ingrown toenails are uncommon in children and infants and are more common in men than in women. Teenagers and young adults are most at risk due to the high level of physical activity. Any toenail can become ingrown, but the condition is usually found in the big toe. [1]
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you:
- Experience severe discomfort in your toe or pus or redness that seems to be spreading
- Have diabetes or any circulation impairment to your lower extremities and experience any foot sore or infection [2]
Treatments
You can typically treat ingrown toenails through home remedies, such as soaking your foot regularly in warm water and applying an antibiotic cream. [2] However, in severe ingrown toenails part of the nail might need to be removed and antibiotics prescribed for infection. Partial nail removal may also be an option, rather then full nail removal. Also a portion of the toenail along with the underlying tissue (nail bed) can be removed to prevent that part of your nail from growing back. This procedure can be done with a chemical, a laser or other methods. [2]
Prevention
Trim your toenails straight across and keep them at a moderate length. Don’t curve your nails to match the shape of the front of your toe especially f you have circulation problems in your feet from disorders such as diabetes or peripheral vascular disease. [2] If you do have this disorders you should see a podiatrist regularly to have your nails professionally trimmed if you can’t trim them yourself.
Wear shoes that fit properly. Shoes that place excessive pressure on your toes or pinch your toes may cause your nails to grow into surrounding tissue. [2] Make sure you buy and wear properly fitted shoes, preferably from a shoe store specializing in fitting shoes for people with foot problems if you have diabetes or peripheral decreased sensation.
Wear protective footwear. If your work puts you at risk of injuring your toes, buy footwear such as steel-toed shoes, which protect your toes. [2]


