MELASMA
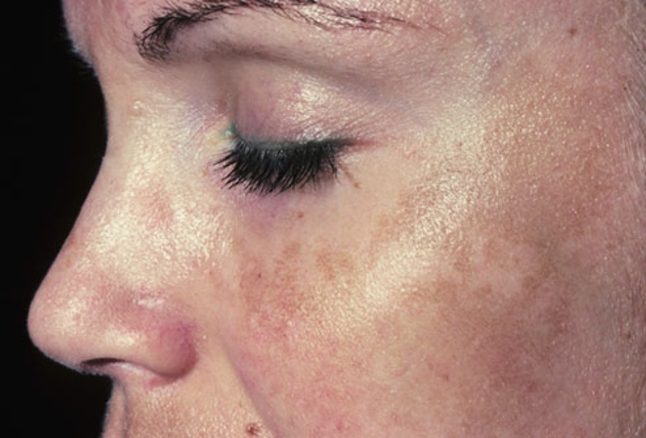
Definition: Melasma is a condition characterized by tan or brown patches (hyperpigmentation), most commonly on the face. Melasma can occur in pregnant women and is often called the “mask of pregnancy;” however, men can also develop this condition. [1]
Other names: Pregnancy Mask, chloasma [1]
Causes
Melasma is a very common skin disorder, especially among women. Young women with brown skin tones are at greatest risk, especially pregnant women or those taking hormone replacement therapy medications. [2]
Melasma is often associated with the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. It is especially common in pregnant women, women who are taking birth control pills (oral contraceptives) and women taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during menopause. [1] Hormones stimulate the production of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in our skin, as they become exposed by the sun. The increased melanin production causes the spotting we see with Melasma. [2]
Sun exposure is also a strong risk factor for melasma and likely worsens the condition. The condition is particularly common in tropical climates due to the large amount of UV radiation. [1]
Symptoms
Generally the symptoms include dark patches and spots on the cheeks, nose, forehead or upper lip. They may develop and worsen over time. [1] A uniform brown color is usually seen and it is most often symmetrical (matching on both sides of the face). [1] Melasma is a purely cosmetic concern. [2] It usually resolves after pregnancy when hormones are back in balance. [1]
Treatment
There are a number of treatments available for melasma. Some include:
- Laser Treatment to remove the discoloration in the skin
- Topical Creams with lightening compounds
- Chemical Peels [2]
Creams
Topical Creams like Hydroquinone Creams containing a combination of tretinoin, kojic acid, and azelaic acid have been shown to improve the appearance of melasma. [1] Tretinoin should not be used in pregnancy. [3] Occasionally, your doctor may recommend topical steroid creams. These bleaching creams are good for bleaching large areas of discoloration. [5]
Topical Retin-A can be good but as well for malasma but it can also be irritating, especially to patients with light skin. In addition, you should never use bleaching creams or products like Retin-A or alpha hydroxy acids (which can also lighten the skin), without first using a sunscreen in the morning because all bleaching creams, Retin-As, and alpha hydroxy acids make you more sensitive to the sun. [5]
Laser Treatment
Lasers are ideal for age spot removal because the melanin pigment is designed to absorb light, and therefore almost any color of laser light can be used to take away brown spots. [3] There are a number of lasers which may be used. For example, the Q-switched lasers are very safe and treat the surface of the skin. The 532nm Nd:YAG laser, which is a green light laser or the 1064 Nd:YAG laser which is an invisible, infrared laser are good options. Other lasers that are used for this include the 755nm Alexandrite Q-switched laser, 694 Ruby Q-switched laser or the Perfecta which is a pulsed-dye laser with a compression hand piece. There are also the Intense Pulsed Light sources which are good at removing brown spots. [3]
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the surface of the skin. The depth of the peel depends on the type of chemical and the method of application. The solution dissolves the damaged, age-spotted surface tissue. The damaged skin is then replaced with a more youthful looking layer. There is usually little downtime from a chemical peel, though you may experience some redness or irritation immediately following the treatment. [4] It may require more than one chemical peel and/or a chemical peel in addition to a lightening cream.
Prevention
Daily sunscreen use not only helps prevent melasma but is crucial in the prevention of skin cancer and wrinkles. [1] Use Sunscreen (ideally SPF 30 or higher) daily. The best way to remember to put on daily sunscreen is to use a moisturizer with sunscreen in it.


