HAIR TRANSPLANT
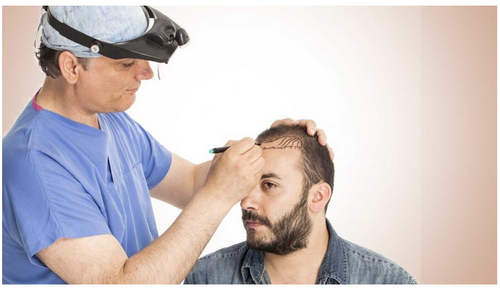
Definition: Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that involves moving skin containing hair follicles from one part of the body (the donor site) to bald or balding parts (the recipient site). [1]
Uses for Hair Transplants
The most common use for hair transplants is to treat male pattern baldness, however female baldness is also commonly treated with hair transplants. This is usually done using grafts containing hair follicles that are resistant to balding are transplanted to bald scalp. Other uses for hair transplants include restoring eyelashes and eyebrows, and facial hair. Hair transplantation grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis surrounding the hair follicle, and many tiny grafts are transplanted rather than a single strip of skin. [1]
Since hair naturally grows in follicles that contain groupings of 1 to 4 hairs, today’s most advanced techniques transplant these groupings (called follicular units). This creates a natural appearance by mimicking nature hair for hair. This recent hair transplant procedure is called Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT). [1]
Causes for Hair Loss
Male and female balding (usually pattern hair loss), are polygenetic disorders of unknown etiology. The age of onset and the rate of hair loss vary, as some patients lose all their hair as early as the 20’s, while other patient have hair that gradual thins over 50 years. Family history of hair loss does not necessary determine the pattern of hair loss in each individual. [4] Male pattern baldness affects approximately 50% of all men, and female-pattern hair loss affects approximately 30-40% of all women. [4]
Donor Hair Harvesting
Donor hair can be harvested in two very different ways:
- Strip Harvesting – In this method a strip of scalp is removed under local anesthesia. The wound is then sutured back together and this piece of scalp tissue is cut in to small pieces for grafts. These are then transplanted back into the area of the patient’s head where the hair is thin. This method will leave a scar in the donor area. The recovery period is around 2 weeks and will require the stitches to be removed. [2]
- FUE Harvesting – (Follicular Unit Extraction) is how hair is harvested for FUT. In this method, individual follicles of hair are removed under local anesthesia using tiny biopsy punches of between 0.6mm and 1.25mm in diameter. Each follicle is then reinserted back in to the scalp in the thinning area using a micro blade. Because this is single follicles there are no visible scars or after surgery pain, with no need to return to the clinic after surgery as there are no stitches to remove. Recovery from FUE/FUT is within 7 days. [2]
The Hair Transplant Procedure
Transplant operations are performed on an outpatient basis sometimes with mild sedation (optional), but usually only with injected topical anesthesia. The scalp is shampooed and then treated with an antibacterial chemical prior to the donor scalp being harvested.
In the usual follicular unit procedure, the surgeon harvests a strip of skin from the posterior (back) of the scalp in an area of good hair growth. The excised strip is about 1–1.5 x 15–30 cm in size. [3] The wound is closed usually by the surgeon and assistants dissect individual follicular unit grafts from the strip. Working with binocular Stereo-microscopes, excess tissue is removed while trying to avoid damage to the follicular cells that will be used for grafting. The latest method of closure of the donor site is called ‘Trichophytic closure’. The procedure typically last about four hours. [3]
FUE harvesting can give very natural results with the right experienced surgeon. In the procedure, the surgeon uses very small micro blades or needles to puncture the sites for receiving the grafts and places them in a predetermined density and pattern. The best surgeons can create a realistic hair pattern. The assistants generally do the final part of the procedure, which is inserting the individual grafts in place. [3] However, the drawback to follicular unit extraction (FUE) transplantation is the limited donor supply and because each follicular unit is removed individually the procedure is much longer. Usually a surgeon will only do 500 grafts per session, and the cost of each graft is almost double that of the standard linear extraction procedure. [3] However there are skilled FUE surgeons that can make up to 4000 FUE in a single mega session. There is literature that suggests 98.7% is the possible live graft outcome rate from FUE. [3]This procedure does not have any long term or major side effects. Taking antibiotics after the procedure can prevent possible complications (infection of the grafts).
During the procedure patients usually feel little or no pain, and can return to work the very next day. The transplanted hair will start to grow in 3 to 6 months, and will have the same strength, color, texture, length, and life span as the hair from the donor area. [1]
Costs
In recent years hair transplants have become less expensive. Prices typically range from $3.00 to $7.00 per graft, with $4 to $5 per graft being about average. [2] Normally surgeons will give patients a deal and the price per graft also drops as the number of grafts increases. A typical surgical session can range from 1,500 to over 4,000 grafts, resulting in a total cost of approximately $6000 to $20000. In India where the costs are still comparatively low, the total cost is less than $3000 for about 5000 grafts. [2] However, to get a cheaper procedure, you are risking your health outside the stringent regulation of the USA.
Future Hair Loss Treatments
Research in gene therapies to alter a person’s genetic vulnerability to hair loss is ongoing. Research is also underway to create multiple hair follicles from one original follicle. This process called “Hair Multiplication” is currently being investigated. [2]
Drug treatments which inhibit the balding process seem more promising. The hair loss drug Propecia (finasteride) has been proven success in slowing and/or stopping hair loss by blocking the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the scalp. [2]
References:
1. www.hairtransplant.com/
2. Bernstein RM, Rassman WR, Seager D, et al. (1998). “Standardizing the classification and description of follicular unit transplantation and mini-micrografting techniques. The American Society for Dermatologic Surgery, Inc”. Dermatol Surg 24 (9): 957–63.
3. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1125960-overview


