SKIN GRAFT
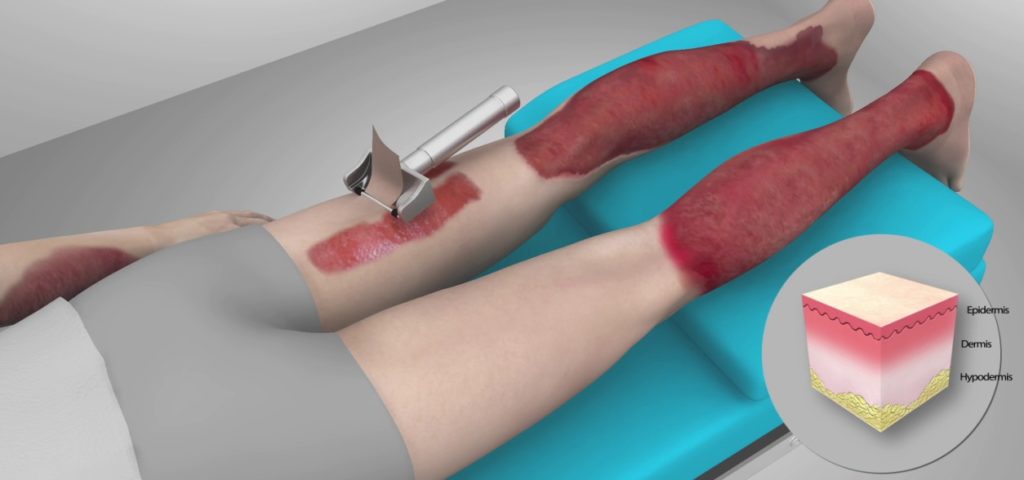
What is a skin graft?
A skin graft is a medical procedure in which a healthy patch of skin, called the donor site, is removed from one part of the body and transplanted to another part of the body to replace the injured skin. Skin graft procedures can be done using two different methods, but the most common procedure is a split-thickness skin graft. With this procedure, the top two layers of skin (epidermis and dermis) are removed from a donor site, which is usually chosen to be an area covered by clothing. The second type of skin graft is a full-thickness skin graft. With this procedure, the skin removed from the donor site includes the muscles and blood supply. A full-thickness skin graft is only used for individuals with deep tissue losses.
Why would you need a skin graft?
Skin graft procedures are done for several reasons but the most common include: burns, ulcers, surgeries (skin cancer and reconstructive) and infections that cause skin loss.
What is the healing process after a skin graft procedure?
The donor site receives a sterile medication for 3 to 5 days and then generally heals on its own in a few weeks. The area where the skin graft was placed has a longer healing time period. The new blood vessels begin growing in 36 hours but acquiring full functionality requires a longer period of time. For a split-thickness skin graft, the area generally needs 3 to 4 weeks to fully set into place. This time frame can vary and individuals may need physical therapy after the procedure to get full range of motion back in the area. The full-thickness skin grafts require longer recovery times and may require up to two weeks of hospital stay.


